During the first year of the TWINRD project, a key focus was on developing methodologies to assess R&D contributions from the different countries and production sectors to green and digital technologies. The process began by collecting publicly available R&D data from sources such as OECD, EUROSTAT, and JRC’s PREDICT, covering 45 countries and up to 114 NACE codes (sectors and sub-aggregates) over the period 1995–2022.
However, across this 28-year period, 21% of the time series were incomplete, and the completion rate for the remaining data was only 38%. To address these gaps, two methodological approaches were applied:
- Parent/Child Model:
- This method used retro- and inter-extrapolation to fill in missing data for time series with at least one available data point.
- Sectoral Similarity Model:
- For sectors with completely missing data, this approach assumed similar R&D investment patterns across countries or country groups.
- Correlations between R&D patent costs and R&D intensity profiles were analyzed across pairs and groups of countries.
Both approaches demonstrated similar reliability in completing missing data. However, since patent data is available only for industrial sectors and J32 (computer programming), direct comparisons were only possible for these sectors. The patent cost approach was ultimately preferred, and R&D data was completed for industrial sectors plus J32 across the initial 45-country sample. This methodology will now be extended to an additional 22 countries with patent data, ensuring comprehensive global coverage of R&D contributions to green and digital technologies.
Next Steps: Splitting R&D Data by Country, Sector, and Technology
The next phase involves disaggregating R&D data by country, sector, and technology. Using patent counts per technology, R&D investments will be allocated across different technologies, assuming that patent costs are sector-specific but not technology-specific.
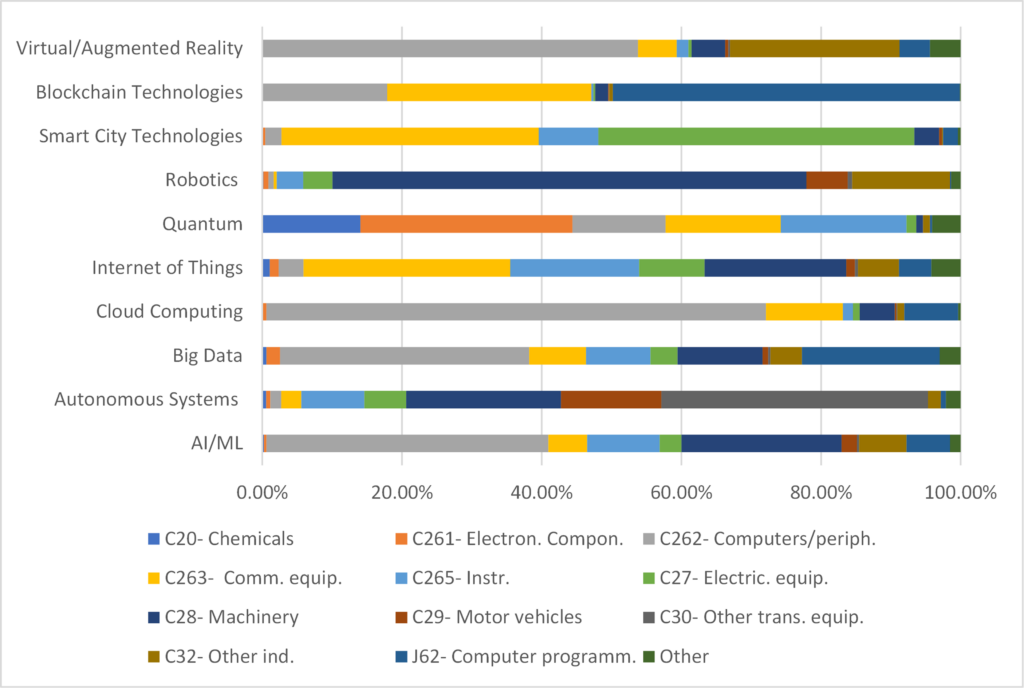
As a preliminary example, the table below illustrates global worldwide sectoral contributions to patents for 4IR technologies in 2018, based on a selection of NACE sectors. Specifically, for AI/ML technologies, 40.38% of global AI/ML-related patents originated from sector C262 (“Computers and Peripheral Equipment”). Under our modeling assumptions, this suggests that approximately 40% of global R&D investment in AI/ML comes from this sector.
Table: Illustration of the relative contribution of NACE sectors to WIPO digital technologies (World level, year 2018)
This work is expected to be completed by June 2025, after which all data will be made publicly available for the scientific community.

